C++ program to check strong number or not
In this example, you will write a C++ program to check whether the user entered integer is a Strong number or not. for example, 1, 2, 145, etc are Strong numbers.
What is a Strong number?
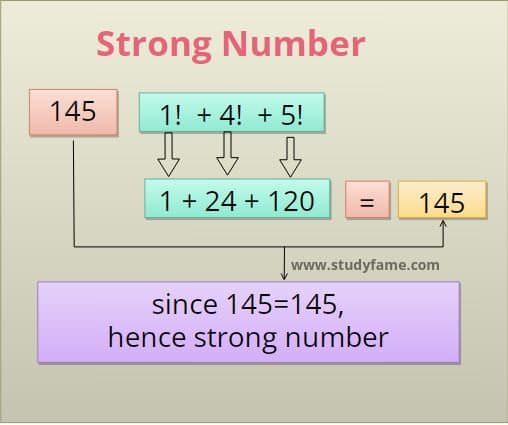
The Sum of the factorial of individual digits of the number is equal to the original number is called a Strong number.
For example 145 = 1! + 4! + 5! i.e 1 + 24 + 120.
Strong number program in C++
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int remainders, fact, sum = 0, i, num, copynum;
cout << "enter the number:";
cin >> num;
copynum = num;
while (num != 0)
{
remainders = num % 10;
fact = 1;
/* find the factorial remainders*/
for (i = 1; i <= remainders; i++)
{
fact = fact * i;
}
/* Add factorial of individual digit */
sum = sum + fact;
num = num / 10;
}
if (sum == copynum) {
cout << copynum << " is strong numbers";
} else {
cout << copynum << " is not strong numbers";
}
return 0;
}
output
enter the number:145 145 is strong numbers
enter the number:123 123 is not strong numbers
Logic to check Strong number.
- Take a number from the user and stored it in variable
num. - Iterate the loop until the
numvalue becomes 0. - Get the last digit of the number and stored it in variable
remainderi.e remainders = num % 10. - find the factorial of the
remainderstored it in variablefact. - now add the factorial value to the
sum. - Remove the last digit of a number i.e
num/10. - repeat steps 3 to 6 until num becomes zero.
C++ program to Check Strong numbers using the function
In this program, you will check Strong Numbers by using User defined function.
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int checkStrongNumber(int num);
int getfactorial(int remainders);
int main() {
int sum, num;
cout << "enter the number:";
cin >> num;
/* call the function */
sum = checkStrongNumber(num);
if (sum == num) {
cout << num << " is strong numbers";
} else {
cout << num << " is not strong numbers";
}
return 0;
}
int getfactorial(int remainders){
int fact=1,i;
for (i = 1; i <= remainders; i++)
{
fact = fact * i;
}
return fact;
}
int checkStrongNumber(int num){
int remainders, fact, sum = 0;
while (num != 0)
{
remainders = num % 10;
/* find the factorial of remainders using get factorial function*/
fact = getfactorial(remainders);
/* Add factorial of individual digit */
sum = sum + fact;
num = num / 10;
}
return sum;
}
Output of this program will same as the above program